Indonesia is emerging as a major player in Southeast Asia, driven by its strategic location, natural resources, and a young, dynamic population. But what factors are propelling its rise, and can it truly become the region’s dominant economic power?
Economic Growth and Stability
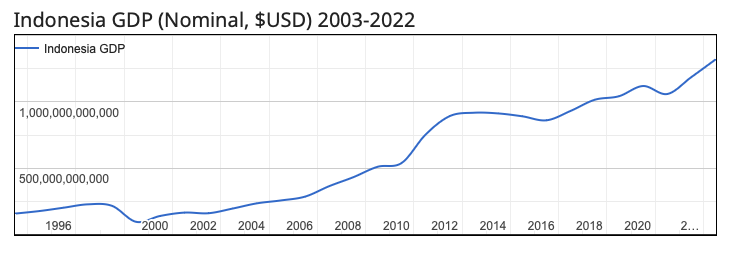
Indonesia’s economy has remained resilient, maintaining growth despite global challenges like COVID-19. Ranked among the largest economies by GDP, it benefits from a growing middle class with increased purchasing power. The government’s infrastructure projects, including highways, airports, and energy facilities, further strengthen domestic and international trade routes.
- Resilience: Steady growth, even during global downturns.
- Domestic Strength: Middle class driving consumption.
- Infrastructure: Projects enhancing connectivity and trade.
Natural Resources and Industry Diversification
While Indonesia is rich in natural resources, the government is diversifying into manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy. These efforts have attracted foreign investment, particularly in automotive and electronics, positioning the country as a hub for innovation.
- Resource Wealth: Leading exporter of coal, palm oil, and natural gas.
- Diversification: Growing investments in technology and manufacturing.
- Foreign Investment: Multinational companies are setting up in Indonesia.
Strategic Location and Geopolitical Influence
Indonesia’s location along vital maritime trade routes gives it geopolitical leverage. As the largest economy in ASEAN, it plays a key role in regional politics and economics. Strong ties with global powers like China and the U.S. also enhance its regional influence.
- Strategic Location: Key player in regional trade.
- ASEAN Leader: Largest economy in Southeast Asia.
- Global Ties: Strengthening relationships with China and the U.S.
Challenges and Opportunities
Indonesia faces challenges such as infrastructure gaps, inefficiencies, and corruption. However, with continued investment in infrastructure and human capital, it is well-positioned to rise as Southeast Asia’s leading economic power.
- Challenges: Infrastructure gaps and corruption.
- Opportunities: Investment in infrastructure and sustainability.
Indonesia’s ascent is evident, with the world closely watching its growing influence regionally and globally.





